Cover photo credits: Goodwin Steel Castings . The title and logo have been added to the original image.
Die Casting Process is a manufacturing technique for producing metal components that are used in everyday use.
The Insight Series
We work with our suppliers to develop products across a wide range of sectors, using different materials and manufacturing techniques.
It is always fascinating to see how each of these products is made—whether it’s the number of hands that touch the product during production or the machines that power the process.
This month, our Insight Series is back! We are focusing on industrial manufacturing and, in particular, the High Pressure Die Casting Process.
Industrial manufacturing continues to grow as part of offshore production. Many companies are now partnering with Asian suppliers to improve margins at the product level while maintaining high-quality standards.
Inside Industrial Manufacturing
Industrial manufacturing covers a broad range of techniques, processes and machinery. The application is similarly broad – engines, components, panels, wheels, tracks – essentially anything that involves the production of metal parts or plastic parts. Imagine, high temperatures, molten metal and large machines pressing., stamping and casting metal! Given the breadth of the topic, we have decided to focus on just one area for this issue.
High Pressure Die Casting Process
High pressure die casting is a quick, reliable and cost-effective manufacturing process for high volume production of metal components, where molten metal is forced under pressure into a securely locked metal die cavity (tool or mould as some people would have heard). It is then held in place by a powerful press until the metal cools and solidifies. After solidification of the metal, the die is unlocked, opened, and the casting extracted automatically.
Applications
Certainly, high-pressure die casting has a wide application, accounting for nearly 50% of all light alloy casting production. This includes engine parts, motorcycle components, household white goods, cookware, and plumbing & heating items, to name a few.
It is also used in many everyday products that you might see around your home. Workers in these factories handle molten metals and always wear protective clothing and eyewear for safety.
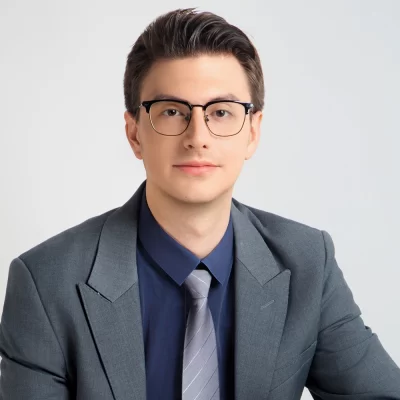
An example of a high-pressure die casting is shown in the illustration below. Here, liquid metal is injected at high speed and pressure into a mould.
The basic equipment includes two vertical platens. Bolsters are mounted on these platens to hold the die halves. One platen is fixed, while the other is movable, which allows the die to open and close during the process.
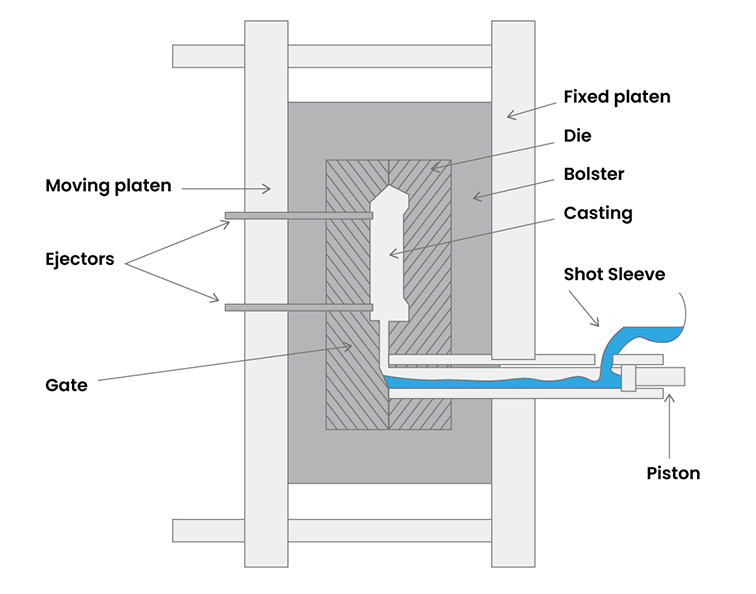
High Pressure Die Casting Process
A specific amount of molten metal is poured into the shot sleeve and then introduced into the die cavity. This is done using a hydraulically driven piston, which forms the required shape.
Unlike traditional handcrafting, much of this process is automated. Workers mainly oversee and operate the machinery rather than manually shaping the product.
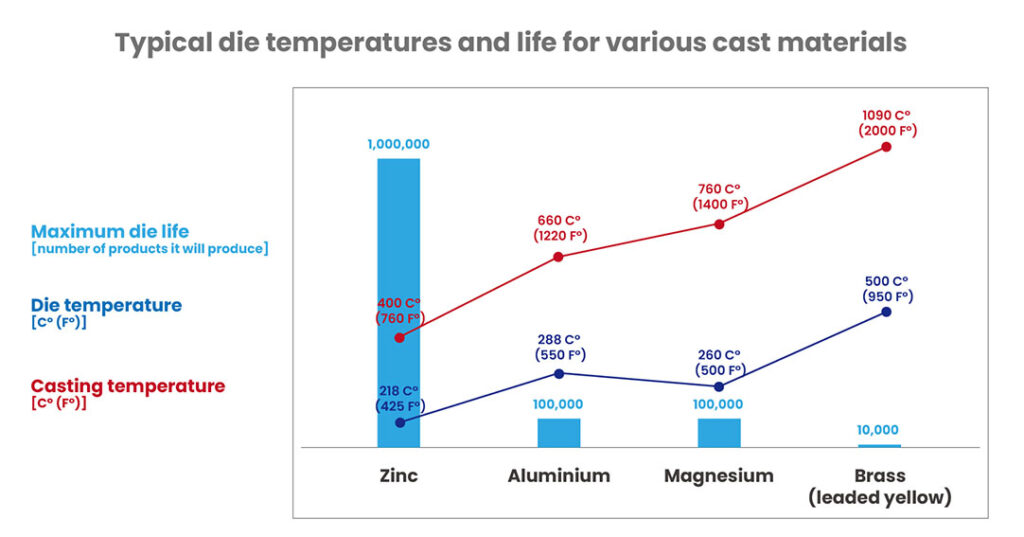
Different metals require different heating levels, and temperatures can reach up to 1,090°C to achieve effective casting.
The table below shows not only the casting temperatures but also the number of products each die can produce before it begins to degrade. At that stage, defects may appear in the final product.
This durability is important. High-pressure die casting can produce large volumes of products before the die needs replacing—a key factor, since dies are expensive to manufacture.
Jelly Sweets
So, have you ever wondered how jelly sweets are made? HPDC has a broad application and even used to make moulds for sweets. This strawberry jelly mould is made from aluminium (non-ferrous) material which is a versatile material that can be heat treated to give added strength together with lightness, corrosion resistance and high conductivity.

The specific casting temperature of this aluminium is 660.3 degrees C. Raw material is supplied in ingot form (left image) then turned into molten metal in a furnace to be transferred into the shot sleeve for the casting process to commence.
The end product is the mould that food manufacturers use to make a jelly sweet – and lots of them!
Advantages of High-Pressure Die Casting Process
As a manufacturing process, high-pressure die casting has a lot of advantages:
- Low Costs. Given the speed of process, and the level of automation, HDPC is able to produce a lot of products out of one mould compared with other casting processes. This reduces the cost per unit, albeit sometimes the capital investment can be on the higher side.Tolerances
- Tolerances. The process is able to produce close dimensional control (the metal fills the cavity) and good surface finish.
- Weight Flexibility. Given the high pressure used in the production, HDPC is able to produce thin wall finishes, which leads to lighter end product, which still maintains rigidity and functionality.
Summary
Certainly, Industrial manufacturing is a fast-growing sector for offshore manufacturing, particularly across Asia where relative share has grown significantly. This is due to the cost reductions being significant but also overlaid with excellent suppliers and quality standards.
At ET2C, we look to provide our clients with insights across our manufacturing base. We already manufacture a range of industrial products for our clients across multiple markets. For more information, please contact us at contact@et2cint.com.

David Young
Position: Group Marketing Director
David W. Young is a recognized thought leader in global sourcing and procurement, sharing expert insights on navigating inflation, managing overheads, and building resilient supply chains. He champions strategic solutions for maximizing business value in a volatile world. LinkedIn or david.y@et2c.com.









